Tianjin Goldensea Hardware Products Co., Ltd
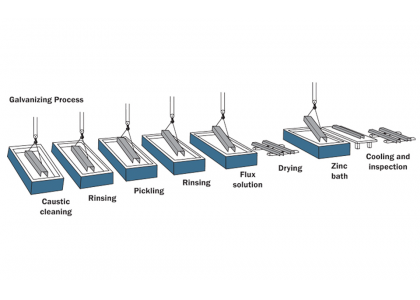
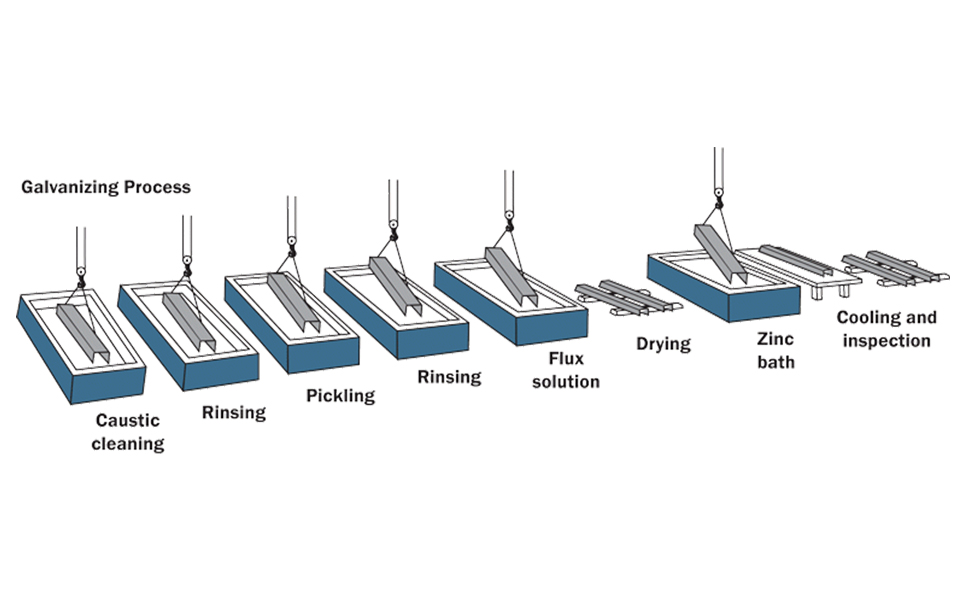
Hot-dip galvanizing is a common anti-corrosion treatment process for fasteners, which is widely used, and its process is as follows:
Workpiece degreasing - washing - pickling - washing - dip plating solvent - drying and preheating - hot dip galvanizing - finishing - cooling - passivation - rinsing - drying - inspection.
In these links, some operational points need to be noted.
In the degreasing link, chemical degreasing or water-based metal degreasing cleaning agent can be used to remove oil, so that the workpiece is completely soaked.
In the pickling process, corrosion inhibitors can be added to prevent excessive corrosion of the matrix and reduce the amount of hydrogen absorption of the iron matrix.
If the two links of degreasing and pickling are not treated well, it may cause poor adhesion of the coating, no zinc plating or zinc layer falling off.
Dip aid plating agent, that is, dip binder, this link can allow the workpiece to maintain a certain activity before dipping, thereby increasing the coating and substrate bonding. In this link, an appropriate amount of glycerin can be added to the plating aid to prevent the evaporation of the plating aid.
The preheating temperature of drying and preheating is generally 120℃-180℃, which is to prevent the workpiece from deformation due to the sharp rise in temperature when dipping, and remove the residual water to prevent the zinc liquid from sputtering.
The hot dip galvanizing process needs to pay attention to controlling the temperature of the zinc solution, the dipping time and the speed of the workpiece moving from the zinc solution. If the temperature is too low, the fluidity of the zinc liquid is poor, the coating will be too thick and uneven, and it is easy to produce flow hanging; If the temperature is too high, the iron loss of the workpiece and the zinc pan will be serious, resulting in a large amount of zinc slag, affecting the quality of the zinc layer, and even unable to dip. Only the appropriate temperature of the zinc liquid, its fluidity is good, the zinc liquid adhesion is strong and easy to leave the workpiece, so that the coating is thin and uniform, the appearance is good, most of the zinc liquid time is at 450℃-470℃, sometimes if the temperature is low, it will be in the zinc liquid many times a small amount of aluminum, to prevent the coating is too thick.
After galvanizing, the workpiece should be finished to remove the surface zinc.
The purpose of passivation is to improve the corrosion resistance of the workpiece, reduce or extend the occurrence time of white rust, and keep the appearance of the zinc layer beautiful.
Cooling is much cooled by water, but the temperature cannot be too low to prevent the workpiece (especially the casting) from shrinking due to cold, resulting in cracking of the matrix tissue.
Qualified hot-dip galvanized fasteners must pass the inspection pass, and their appearance should be bright and detailed, without flow hanging and wrinkling, uniform coating thickness, and no cracks and plating falling off during tapping or pressure detection.